Every project grows to a point it needs to support a Fulltext Search. And once you reach the point you'll need to give estimates.
But have you ever built such a thing? How do you extract data from PDF files? Microsoft Word? Microsoft Excel? Microsoft PowerPoint? RTF? JPEG Images? How do you call Elasticsearch and process its results?
In this article I will develop a simple Fulltext Search Frontend and Backend using ASP.NET Core, Angular 9, Elasticsearch, Tesseract and PostgreSQL. It is meant as a basis for quick prototyping and iterate on ideas.
You can find all code in my GitHub repository at:
Table of contents
What we are going to build
Let's take a look at what we will build.
If we want to make documents searchable, we need a way to send documents from a client to a server, so we will build a small dialog for uploading files and adding some metadata like keywords and a document title:
Once we uploaded a file, we want to know the status. Is the document indexed? Is it still scheduled for indexing? Or was there a Server failure, that needs to be reported? So we add a component to see the status for each document:
What's a modern search without getting suggestions? Suggestions can help users find interesting content or reduce typos. So we'll also add an Auto-Completion box:
And what are we building all this for?
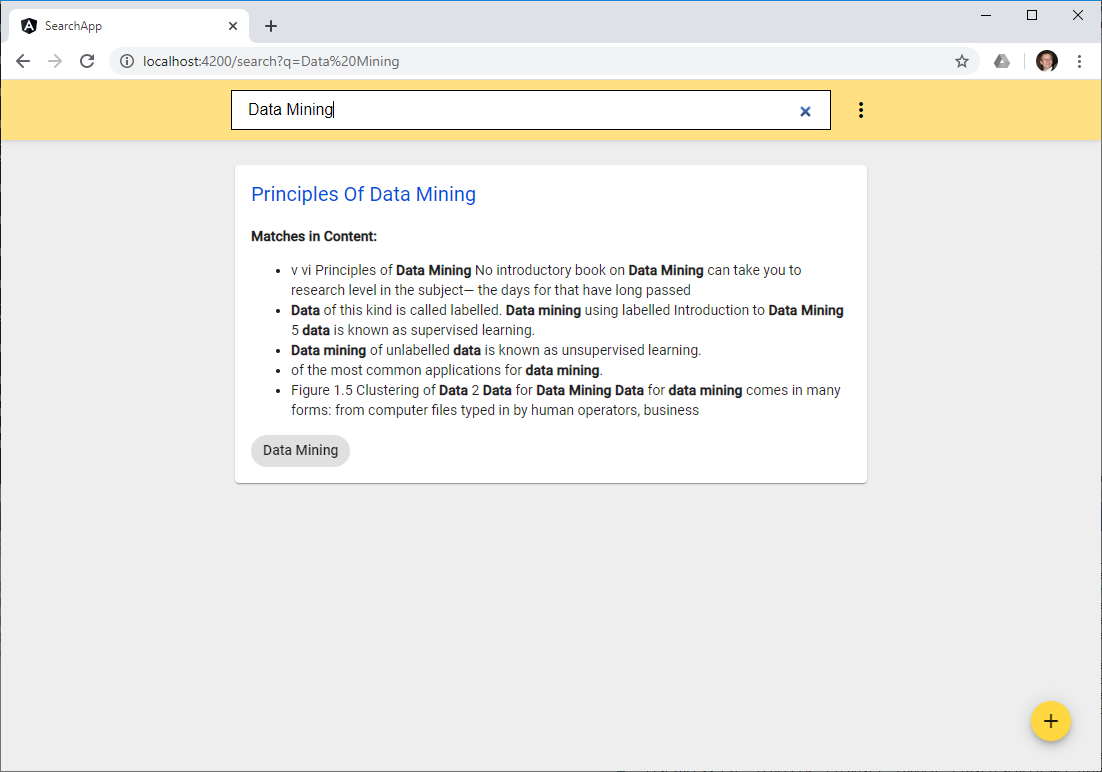
Exactely, for getting search results on the uploaded data!
The search results will contain the highlighted matches from the Elasticsearch server:
Frontend
The Frontend is written with Angular 9. And it should be obvious, that I am not a great UI designer or CSS wizard. Just take a look at my minimal website... and even that took me weeks to build!
That's why the project uses the Angular Material components:
Also note, that I am not using ngrx or any Redux libraries in the code, just because it would overcomplicate things. It's all basic Angular.
Preparation
Adding Paths to the tsconfig.json
When importing components and services in Angular I want to write @app and @environments for referencing the app
and environment folders instead of having to use relative paths. You can set this by adding a section paths in the
tsconfig.json, like this:
{
"compileOnSave": false,
"compilerOptions": {
"paths": {
"@app/*": [
"src/app/*"
],
"@environments/*": [
"src/environments/*"
]
}
},
Configuring the environment
Angular uses the environment.ts and environment.prod.ts to set environment settings for debug and
prod targets. We only need to add a apiUrl key for now, which defines the Backend API endpoint.
The environment.ts for debugging looks like this:
export const environment = {
production: false,
apiUrl: "http://localhost:9000/api"
};
And the environment.prod.ts for the production builds looks like this:
export const environment = {
production: true,
apiUrl: "http://localhost:9000/api"
};
The Data Model
I am going to keep it very simple for this application and put all data contracts in a global file called
app.model.ts. In a larger application you probably want to modularize your Angular application, but this
is sufficient for now.
The interfaces SearchStateEnum, SearchQuery, SearchResults and SearchResult hold the
Search results for a given query:
export enum SearchStateEnum {
Loading = "loading",
Finished = "finished",
Error = "error"
}
export interface SearchQuery {
state: SearchStateEnum;
data: SearchResults;
error: string;
}
export interface SearchResults {
query: string;
results: SearchResult[];
}
export interface SearchResult {
identifier: string;
title: string;
matches: string[];
keywords: string[];
url: string;
type: string;
}
For the suggestions in the Auto-Complete Box we define two interfaces SearchSuggestions and SearchSuggestion:
export interface SearchSuggestions {
query: string;
results: SearchSuggestion[];
}
export interface SearchSuggestion {
text: string;
highlight: string;
}
And to get an overview of indexed documents we are defining a DocumentStatus interface:
export enum StatusEnum {
None = "none",
ScheduledIndex = "scheduledIndex",
ScheduledDelete = "scheduledDelete",
Indexed = "indexed",
Failed = "failed",
Deleted = "deleted"
}
export interface DocumentStatus {
id: number;
filename: string;
title: string;
isOcrRequested: boolean;
status: StatusEnum;
}
Services
One way to pass data between Angular components is to use a shared services, like described in the Angular Guide:
We need to pass the search term to the child components, so we define SearchService. In the file
service/search.service.ts we are using a BehaviorSubject, which replays the last search query
to all subscribers and initially starts with an empty search term.
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
import { Subject, Observable, BehaviorSubject } from 'rxjs';
import { share } from 'rxjs/operators';
@Injectable()
export class SearchService {
private searchSubmittings$ = new BehaviorSubject<{ term: string }>({ term: null });
submitSearch(term: string) {
this.searchSubmittings$.next({ term });
}
onSearchSubmit(): Observable<{ term: string }> {
return this.searchSubmittings$.pipe(share());
}
}
Routes
Next we define the routes for the application. There are only two routes:
/searchfor the actual search./statusfor the status of indexed documents.
The Angular CLI generates a app-routing.module.ts file, where the routes can be defined:
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { Routes, RouterModule } from '@angular/router';
import { SearchComponent } from '@app/components/search/search.component';
import { DocumentStatusComponent } from './components/document-status/document-status.component';
const routes: Routes = [
{ path: '',
pathMatch: 'full',
redirectTo: "search"
},
{
path: 'search',
component: SearchComponent
},
{
path: 'status',
component: DocumentStatusComponent
}
];
@NgModule({
imports: [RouterModule.forRoot(routes)],
exports: [RouterModule]
})
export class AppRoutingModule { }
Components
AppComponent
The AppComponent is going to host all other child components.
It is going to contain a:
- An
<input>withtype="search"in a search bar. - A
<mat-menu>to navigate between pages. - A
<router-outlet>to host child components. - A Floating Action Button (FAB) to show a file upload dialog.
The Angular Material <mat-autocomplete> component will be used to display the suggestions.
The template is defined in the file app.component.html:
<div class="search-container" fxLayout="column">
<div class="search-bar" fxLayout="row" fxLayoutAlign="center center">
<input #search type="search" (keyup.enter)="onKeyupEnter(search.value)" [formControl]="control" [matAutocomplete]="auto">
<mat-autocomplete #auto="matAutocomplete">
<ng-container *ngIf="suggestions$ | async as suggestions">
<mat-option *ngFor="let suggestion of suggestions?.results" [value]="suggestion.text">
<span [innerHtml]="suggestion.highlight"></span>
</mat-option>
</ng-container>
</mat-autocomplete>
<button mat-icon-button [matMenuTriggerFor]="menu" aria-label="Example icon-button with a menu">
<mat-icon>more_vert</mat-icon>
</button>
<mat-menu #menu="matMenu">
<button mat-menu-item (click)="openFileUploadDialog()">
<mat-icon>add</mat-icon>
<span>Upload Document</span>
</button>
<button mat-menu-item routerLink="/status">
<mat-icon>schedule</mat-icon>
<span>Document Status</span>
</button>
</mat-menu>
</div>
<div>
<router-outlet></router-outlet>
</div>
</div>
<button class="add-button" mat-mini-fab aria-label="Upload Button with Attachment Icon"
(click)="openFileUploadDialog()">
<mat-icon>add</mat-icon>
</button>
Then we add some styling to the components in the file app.component.scss:
@import '~@angular/material/theming';
$accent: mat-palette($mat-amber);
.search-container {
height: auto;
}
.search-bar {
height: 60px;
background-color: mat-color($accent, 200);
box-shadow: 0 1px 2px rgba(0,0,0,0.05),0 1px 4px rgba(0,0,0,0.05),0 2px 8px rgba(0,0,0,0.05);
}
input {
border: solid 1px black;
outline: none;
margin: 10px;
padding: 6px 16px;
width: 100%;
max-width: 600px;
height: 40px;
font-size: 16px;
}
.add-button {
position: fixed;
top: auto;
right: 30px;
bottom: 30px;
left: auto;
}
And in the class component file at app.component.ts we wire things up.
How do the suggestions for the <mat-autocomplete> work? A FormControl in Angular provides the Observable valueChanges,
by using debounceTime(300) we make sure not every single keystroke is sent to the server but only after 300ms. We are then
using the switchMap operator to query the Suggestions API endpoint.
Now when a user enters a query I am using Router navigation to navigate to the /search page. This has the nice side-effect,
that you can use /search?q=MySearch in a URL to search for documents containing MySearch. The ngOnInit method then
emits the search term to the SearchService.
Make sure to always use the catchError operator when defining Observables, because you don't want an error to silently kill your
atuo-complete or other subscriptions.
import { Component, ViewChild } from '@angular/core';
import { SearchSuggestions } from '@app/app.model';
import { HttpClient } from '@angular/common/http';
import { environment } from '@environments/environment';
import { Router, ActivatedRoute } from '@angular/router';
import { Observable, of } from 'rxjs';
import { switchMap, debounceTime, catchError, map, filter } from 'rxjs/operators';
import { FormControl } from '@angular/forms';
import { MatDialog } from '@angular/material/dialog';
import { MatAutocompleteTrigger } from '@angular/material/autocomplete';
import { FileUploadComponent } from './components/file-upload/file-upload.component';
import { DocumentStatusComponent } from './components/document-status/document-status.component';
import { SearchService } from './services/search.service';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./app.component.scss']
})
export class AppComponent {
destroy$: Observable<void>;
control = new FormControl();
query$: Observable<string>;
suggestions$: Observable<SearchSuggestions>;
@ViewChild('search', { read: MatAutocompleteTrigger })
autoComplete: MatAutocompleteTrigger;
constructor(private route: ActivatedRoute,
private searchService: SearchService,
private dialog: MatDialog,
private router: Router,
private httpClient: HttpClient) {
}
ngOnInit(): void {
this.route.queryParams
.pipe(
map(params => params['q']),
filter(query => !!query)
)
.subscribe(query => {
this.control.setValue(query);
this.searchService.submitSearch(query);
});
this.suggestions$ = this.control.valueChanges
.pipe(
debounceTime(300), // Debounce time to not send every keystroke ...
switchMap(value => this
.getSuggestions(value)
.pipe(catchError(() => of(<SearchSuggestions>{ query: value, results: []}))))
);
}
onKeyupEnter(value: string): void {
if(!!this.autoComplete) {
this.autoComplete.closePanel();
}
// Instead of firing the Search directly, let's update the Route instead:
this.router.navigate(['/search'], { queryParams: { q: value } });
}
getSuggestions(query: string): Observable<SearchSuggestions> {
if (!query) {
return of(null);
}
return this.httpClient
// Get the Results from the API:
.get<SearchSuggestions>(`${environment.apiUrl}/suggest`, {
params: {
q: query
}
})
.pipe(catchError((err) => {
console.error(`An error occured while fetching suggestions: ${err}`);
return of(<SearchSuggestions>{ query: query, results: []})
}));
}
openFileUploadDialog() {
this.dialog.open(FileUploadComponent);
}
openDocumentStatusDialog() {
this.dialog.open(DocumentStatusComponent);
}
}
SearchComponent
The SearchComponent shows the results of a query.
First let's take a look at the data model again:
export enum SearchStateEnum {
Loading = "loading",
Finished = "finished",
Error = "error"
}
export interface SearchQuery {
state: SearchStateEnum;
data: SearchResults;
error: string;
}
export interface SearchResults {
query: string;
results: SearchResult[];
}
export interface SearchResult {
identifier: string;
title: string;
matches: string[];
keywords: string[];
url: string;
type: string;
}
The SearchStateEnum defines three states a query can have:
LoadingFinishedError
Based on the state we want to give the user some feedback:
- Is the search currently being processed?
- Has the search finished successfully?
- Has the search finished successfully without results?
- Has the search run into an error?
In the template components/search/search.component.html you'll see, that these different states can be handeled by simply using a [ngIf].
<div fxFill fxLayout="column" style="padding-top: 25px;">
<ng-container *ngIf="query$ | async as query">
<!-- -->
<ng-template [ngIf]="query.state == 'loading'">
<div fxFlex fxLayout="row" fxLayoutAlign="center" style="margin-bottom:25px;">
<mat-spinner></mat-spinner>
</div>
</ng-template>
<!-- There was an error processing this request -->
<ng-template [ngIf]="query.state == 'error'">
<div fxFlex fxLayout="row" fxLayoutAlign="center" style="margin-bottom:25px;">
<p>We are very sorry... There was an error processing the request. Maybe try again later? 😓</p>
</div>
</ng-template>
<!--No results found -->
<ng-template [ngIf]="query.state == 'finished' && query.data?.results.length == 0">
<div fxFlex fxLayout="row" fxLayoutAlign="center" style="margin-bottom:25px;">
<p>This query has no results. Maybe try a different one? 😓</p>
</div>
</ng-template>
<ng-template [ngIf]="query.state == 'finished' && query.data?.results.length > 0">
<div *ngFor="let result of query.data?.results" fxFlex fxLayout="row" style="margin-bottom:25px;">
<div fxFlex fxLayoutAlign="center">
<mat-card class="search-result">
<mat-card-content>
<div class="search-result-header" fxLayout="column">
<h3><a class="search-link" href="{{result.url}}">{{result.title}}</a></h3>
</div>
<div>
<br />
<p><strong>Matches in Content:</strong></p>
<ul>
<li *ngFor="let match of result?.matches"><span [innerHtml]="match"></span></li>
</ul>
</div>
<div>
<mat-chip-list aria-label="Keywords">
<mat-chip *ngFor="let keyword of result?.keywords" color="accent">{{keyword}}</mat-chip>
</mat-chip-list>
</div>
</mat-card-content>
<mat-card-actions>
</mat-card-actions>
</mat-card>
</div>
</div>
</ng-template>
</ng-container>
</div>
We style the search results in the components/search/search.component.scss, by adding some colors and paddings
.search-result {
width: 600px;
}
.search-results {
background-color: #eee;
height: 100%;
padding: 25px;
}
.search-link {
color: rgb(2, 80, 224);
text-decoration: none;
&:visited {
color: rgb(2, 80, 224);
}
}
h3 {
margin: 0;
font-size: 20px;
line-height: 1.3;
}
.mat-card-content {
margin: 0;
word-wrap: break-word;
}
p {
margin: 0;
}
And finally the TypeScript file for the SearchComponent in components/search/search.component.ts is very concise.
import { Component, OnInit, OnDestroy } from '@angular/core';
import { SearchResults, SearchStateEnum, SearchQuery } from '@app/app.model';
import { HttpClient } from '@angular/common/http';
import { environment } from '@environments/environment';
import { Observable, of, concat, Subject } from 'rxjs';
import { map, switchMap, filter, catchError, takeUntil } from 'rxjs/operators';
import { FormControl } from '@angular/forms';
import { SearchService } from '@app/services/search.service';
@Component({
selector: 'app-search',
templateUrl: './search.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./search.component.scss']
})
export class SearchComponent implements OnInit, OnDestroy {
destroy$ = new Subject<void>();
control = new FormControl();
query$: Observable<SearchQuery>;
constructor(private httpClient: HttpClient, private searchService: SearchService) {
}
ngOnInit(): void {
this.query$ = this.searchService.onSearchSubmit()
.pipe(
filter(query => !!query.term),
switchMap(query =>
concat(
of(<SearchQuery>{ state: SearchStateEnum.Loading }),
this.doSearch(query.term).pipe(
map(results => <SearchQuery>{state: SearchStateEnum.Finished, data: results}),
catchError(err => of(<SearchQuery>{ state: SearchStateEnum.Error, error: err }))
)
)
),
takeUntil(this.destroy$)
);
}
doSearch(query: string): Observable<SearchResults> {
return this.httpClient
.get<SearchResults>(`${environment.apiUrl}/search`, {
params: {
q: query
}
});
}
ngOnDestroy() {
this.destroy$.next();
this.destroy$.complete();
}
}
I know the Observable in ngOnInit looks a bit frightening, so let's dissect it a bit.
The component get's a SearchService injected, which provides a public method searchService.onSearchSubmit(). This is
an Observable, that emits search terms entered probably in some other component. Now think in Streams:
- The
SearchServiceemits a new search term ... - ... we check if the search term is not empty or undefined using the
filteroperator. - ... we then transform the
Observablewith the search term into anObservable<SearchQuery>. - ... inside the
switchMapwe are usingconcatMap.concatMapmakes sure the following operators evaluate sequentially. - ... we start by emitting a
SearchQueryin theLoadingstate. - ... we then query the API endpoint using
doSearchmethod, which returns us theSearchResults. - ... by using the
mapoperator we are transforming theSearchResultsinto a finishedSearchQuery. - ... if an error occurs we are returning a
SearchQueryin the error state. - ... we listen for the stream until the component is destroyed. The
takeUntil(destroy$)pattern for unsubscribing streams was taken from RxJS samples.
Now you might ask yourself: But where do you actually bind the data to the template?
This is done by using Angulars built-in async pipe:
<ng-container *ngIf="query$ | async as query">
<!-- Work the SearchQuery ... -->
</ng-container>
FileUploadComponent
The file upload is a bit tricky and probably hard to digest for the "pure RESTful" API folk.
The easiest way to upload files is to use, what the browser already offers.
So I am sending a multipart/form-data HTTP request to an endpoint and send all values in form fields.
Basically I need ...
- An
<input>for the document title. - A
<mat-chip-list>for a list of suggestions. - A checkbox, that signals if OCR should be applied or not.
- An
<input>withtype="file"to upload a File
The Component template is defined in components/file-upload/file-upload-component.html:
<h2>Add a Document to the Search Index</h2>
<form [formGroup]="fileUploadForm" (ngSubmit)="onSubmit()">
<div fxLayout="column" class="file-input-container">
<div fxLayout="column">
<mat-form-field fxFlex>
<input matInput formControlName="title" type="text" placeholder="Document Title">
</mat-form-field>
</div>
<div fxLayout="column">
<mat-form-field fxFlex>
<mat-chip-list #chipList aria-label="Suggestions" formControlName="suggestions">
<mat-chip *ngFor="let suggestion of fileUploadForm.get('suggestions').value" [selectable]="true" [removable]="true" (removed)="onRemoveSuggestion(suggestion)">
{{suggestion}}
<mat-icon matChipRemove>cancel</mat-icon>
</mat-chip>
<input class="min-chips-height" placeholder="Suggestions"
[matChipInputFor]="chipList"
[matChipInputSeparatorKeyCodes]="separatorKeysCodes"
[matChipInputAddOnBlur]="true"
(matChipInputTokenEnd)="onAddSuggestion($event)">
</mat-chip-list>
</mat-form-field>
</div>
<div fxLayout="row">
<input #fileInput id="fileInput" type="file" [hidden]="true" (change)="onFileInputChange($event)">
<mat-form-field fxFlex [floatLabel]="'never'">
<input matInput type="text" formControlName="file" (click)="fileInput.click()"
placeholder="Please Select a File ..." readonly>
</mat-form-field>
<button mat-mini-fab aria-label="Upload Button with Attachment Icon" (click)="fileInput.click()">
<mat-icon>attach_file</mat-icon>
</button>
</div>
<div fxLayout="column" fxLayoutAlign="center start">
<div style="margin: 20px">
<mat-checkbox color="primary" formControlName="ocr">Add OCR Data to Search Index</mat-checkbox>
</div>
</div>
<div fxLayout="column">
<button type="submit" mat-raised-button color="accent" [disabled]="isFileUploading">Index Document</button>
</div>
</div>
</form>
The components styles are defined in components/file-upload/file-upload-component.scss:
.file-input-container {
width: 500px;
margin: 25px;
}
.mat-form-field-padding {
margin: 15px;
}
And the component class is defined in the TypeScript file components/file-upload/file-upload-component.ts.
Again there is no magic involved:
- Reactive Forms are used to bind the
<input>values. - The
<mat-chip-list>code is copied from: - A
FormDataobject is sent to the endpoint${environment.apiUrl}/index
import { COMMA, ENTER } from '@angular/cdk/keycodes';
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { HttpClient } from '@angular/common/http';
import { environment } from '@environments/environment';
import { FormControl, FormGroup, Validators, AbstractControl } from '@angular/forms';
import { MatDialogRef } from '@angular/material/dialog';
import { MatChipInputEvent } from '@angular/material/chips';
import { StringUtils } from '@app/utils/string-utils';
@Component({
selector: 'app-fileupload',
templateUrl: './file-upload.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./file-upload.component.scss']
})
export class FileUploadComponent {
file: File;
separatorKeysCodes: number[] = [ENTER, COMMA];
fileUploadForm = new FormGroup({
title: new FormControl('', Validators.required),
suggestions: new FormControl([], Validators.required),
file: new FormControl('', Validators.required),
ocr: new FormControl(false)
});
isFileUploading: boolean = false;
constructor(public dialogRef: MatDialogRef<FileUploadComponent>, private httpClient: HttpClient) {
}
onFileInputChange(fileInputEvent: any): void {
this.file = fileInputEvent.target.files[0];
this.fileControl.setValue(this.file?.name);
}
onAddSuggestion(event: MatChipInputEvent): void {
const input = event.input;
const value = event.value;
if (!StringUtils.isNullOrWhitespace(value)) {
this.suggestionsControl.setErrors(null);
this.suggestionsControl.value.push(value.trim());
}
if (input) {
input.value = '';
}
this.suggestionsControl.updateValueAndValidity();
}
onRemoveSuggestion(suggestion: string): void {
const index = this.suggestionsControl.value.indexOf(suggestion);
if (index >= 0) {
this.suggestionsControl.value.splice(index, 1);
}
this.suggestionsControl.updateValueAndValidity();
}
onSubmit(): void {
if (this.fileUploadForm.invalid) {
return;
}
this.isFileUploading = true;
this.httpClient
.post<any>(`${environment.apiUrl}/index`, this.buildRequestFormData())
.subscribe(x => {
this.isFileUploading = false;
this.dialogRef.close();
})
}
buildRequestFormData(): FormData {
const formData = new FormData();
formData.append('title', this.titleControl.value);
formData.append('suggestions', this.getCommaSeparatedSuggestions(this.suggestionsControl.value));
formData.append('file', this.file);
formData.append('isOcrRequested', this.ocrControl.value);
return formData;
}
getCommaSeparatedSuggestions(values: string[]): string {
return values
.map(x => `"${x}"`)
.join(",");
}
get titleControl(): AbstractControl {
return this.fileUploadForm.get('title');
}
get suggestionsControl(): AbstractControl {
return this.fileUploadForm.get('suggestions');
}
get fileControl(): AbstractControl {
return this.fileUploadForm.get('file');
}
get ocrControl(): AbstractControl {
return this.fileUploadForm.get('ocr');
}
}
Document Status
As a user you want to get some feedback what happened to my upload or what's happening right now. Has my document been processed yet? How many documents failed to process and what's the reason? You probably want to delete documents altogether or re-run some indexing.
For this we are using a <mat-table> containing the relevant bits of data in the template file components/document-status/document-status.component.html:
<div fxFill fxLayout="column">
<div fxFlex fxLayout="row" style="margin:25px;">
<div fxFlex *ngIf="isDataSourceLoading" fxLayoutAlign="center">
<mat-spinner></mat-spinner>
</div>
<div *ngIf="!isDataSourceLoading" fxFlex>
<table mat-table [dataSource]="dataSource" class="mat-elevation-z8">
<ng-container matColumnDef="select">
<th mat-header-cell *matHeaderCellDef>
<mat-checkbox color="primary" (change)="$event ? masterToggle() : null"
[checked]="selection.hasValue() && isAllSelected()"
[indeterminate]="selection.hasValue() && !isAllSelected()" [aria-label]="checkboxLabel()">
</mat-checkbox>
</th>
<td mat-cell *matCellDef="let row">
<mat-checkbox color="primary" (click)="$event.stopPropagation()"
(change)="$event ? selection.toggle(row) : null" [checked]="selection.isSelected(row)"
[aria-label]="checkboxLabel(row)">
</mat-checkbox>
</td>
</ng-container>
<ng-container matColumnDef="id">
<th mat-header-cell *matHeaderCellDef> Document ID </th>
<td mat-cell *matCellDef="let element"> {{element.id}} </td>
</ng-container>
<ng-container matColumnDef="title">
<th mat-header-cell *matHeaderCellDef> Title </th>
<td mat-cell *matCellDef="let element"> {{element.title}} </td>
</ng-container>
<ng-container matColumnDef="filename">
<th mat-header-cell *matHeaderCellDef> Filename </th>
<td mat-cell *matCellDef="let element"> {{element.filename}} </td>
</ng-container>
<ng-container matColumnDef="isOcrRequested">
<th mat-header-cell *matHeaderCellDef> Additional OCR </th>
<td mat-cell *matCellDef="let element">
<mat-checkbox color="primary" [checked]="element.isOcrRequested" [disableRipple]="true"
(click)="$event.preventDefault()"> </mat-checkbox>
</td>
</ng-container>
<ng-container matColumnDef="status">
<th mat-header-cell *matHeaderCellDef> Status </th>
<td mat-cell *matCellDef="let element"> {{element.status}} </td>
</ng-container>
<tr mat-header-row *matHeaderRowDef="displayedColumns; sticky: true"></tr>
<tr mat-row *matRowDef="let row; columns: displayedColumns;" (click)="selection.toggle(row)">
</tr>
</table>
</div>
</div>
<div fxFlex fxLayout="row" style="margin:25px;" fxLayoutAlign="end center" fxLayoutGap="25px">
<button mat-raised-button color="accent" (click)="scheduleSelectedDocuments()">Re-Index Documents (Alt + R)</button>
<button mat-raised-button color="accent" (click)="removeSelectedDocuments()">Remove Documents (Alt + Del)</button>
</div>
</div>
The styling in components/document-status/document-status.component.scss sets the column width:
.document-status-container {
margin: 25px;
}
.mat-form-field-padding {
margin: 15px;
}
.min-chips-height {
min-height: 50px;
}
table {
width: 100%;
}
td.mat-column-select {
width: 50px;
}
td.mat-column-documentId {
width: 300px;
}
td.mat-column-filename {
width: 400px;
}
td.mat-column-isOcrRequested {
width: 100px;
}
td.mat-column-status {
width: 150px;
}
In the class component file at components/document-status/document-status.component.ts the Document Status is loaded from
the API endpoint /status. Initially the entire table is reloaded in the ngOnInit method. Every five seconds only the
state of each document is updated, so we do not override current selections.
Keyboard Shortcuts often make life a lot easier for Power Users. So if you are designing UIs make sure to also include Keyboard shortcuts for repititive tasks, so users don't get a Carpal tunnel syndrome.
import { Component, OnInit, HostListener, OnDestroy, ChangeDetectorRef } from '@angular/core';
import { HttpClient } from '@angular/common/http';
import { environment } from '@environments/environment';
import { MatTableDataSource } from '@angular/material/table';
import { SelectionModel } from '@angular/cdk/collections';
import { DocumentStatus } from '@app/app.model';
import { catchError, concatMap, mergeMap, toArray, tap, takeUntil } from 'rxjs/operators';
import { of, from, Subject, interval } from 'rxjs';
@Component({
selector: 'app-document-status',
templateUrl: './document-status.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./document-status.component.scss']
})
export class DocumentStatusComponent implements OnInit, OnDestroy {
private destroy$ = new Subject<void>();
displayedColumns: string[] = ['select', 'id', 'title', 'filename', 'isOcrRequested', 'status'];
isDataSourceLoading: boolean = false;
dataSource = new MatTableDataSource<DocumentStatus>();
selection = new SelectionModel<DocumentStatus>(true, []);
constructor(private httpClient: HttpClient, private changeDetectorRefs: ChangeDetectorRef) {
}
ngOnInit(): void {
interval(5000)
.pipe(takeUntil(this.destroy$))
.subscribe(() => this.reloadStatusValues());
this.reloadDataTable();
}
reloadDataTable() {
this.selection.clear();
this.httpClient
.get<DocumentStatus[]>(`${environment.apiUrl}/status`)
.pipe(
catchError(() => of<DocumentStatus[]>([])))
.subscribe(data => {
this.dataSource.data = data;
});
}
reloadStatusValues() {
this.httpClient
.get<DocumentStatus[]>(`${environment.apiUrl}/status`)
.pipe(
catchError(() => of<DocumentStatus[]>([])))
.subscribe(data => {
const status = new Map(data.map(i => [i.id, i.status]));
this.dataSource.data
.forEach(row => {
if (status.has(row.id)) {
row.status = status.get(row.id);
}
});
this.changeDetectorRefs.detectChanges();
});
}
/** Whether the number of selected elements matches the total number of rows. */
isAllSelected() {
const numSelected = this.selection.selected.length;
const numRows = this.dataSource.data.length;
return numSelected === numRows;
}
/** Selects all rows if they are not all selected; otherwise clear selection. */
masterToggle() {
this.isAllSelected() ?
this.selection.clear() :
this.dataSource.data.forEach(row => this.selection.select(row));
}
/** The label for the checkbox on the passed row */
checkboxLabel(row?: DocumentStatus): string {
if (!row) {
return `${this.isAllSelected() ? 'select' : 'deselect'} all`;
}
return `${this.selection.isSelected(row) ? 'deselect' : 'select'} row ${row.id}`;
}
@HostListener('document:keyup', ['$event'])
handleKeyboardEvent(event: KeyboardEvent) {
if (event.altKey && event.key === 'Delete') {
this.removeSelectedDocuments();
}
if (event.altKey && (event.key === 'r' || event.key === 'R')) {
this.scheduleSelectedDocuments();
}
}
removeSelectedDocuments() {
var documentsToRemove = this.selection.selected
from(documentsToRemove)
.pipe(
mergeMap(x => this.httpClient.delete(`${environment.apiUrl}/status/${x.id}`)),
toArray()
)
.subscribe(() => this.reloadDataTable());
}
scheduleSelectedDocuments() {
var documentsToIndex = this.selection.selected
from(documentsToIndex)
.pipe(
mergeMap(x => this.httpClient.post<any>(`${environment.apiUrl}/status/${x.id}/index`, [])),
toArray()
)
.subscribe(() => this.reloadDataTable());
}
ngOnDestroy() {
this.destroy$.next();
this.destroy$.complete();
}
}
Module
The app.module.ts now imports all Angular Material dependencies, provides the SearchService and
declares the AppComponent, SearchComponent, FileUploadComponent and DocumentStatusComponent:
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { FormsModule, ReactiveFormsModule } from '@angular/forms';
import { HttpClientModule } from '@angular/common/http';
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { AppRoutingModule } from './app-routing.module';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import { BrowserAnimationsModule } from '@angular/platform-browser/animations';
import { FlexLayoutModule } from '@angular/flex-layout';
import { MatDialogModule } from '@angular/material/dialog';
import { MatInputModule } from '@angular/material/input';
import { MatButtonModule } from '@angular/material/button';
import { MatChipsModule } from '@angular/material/chips';
import { MatIconModule } from '@angular/material/icon';
import { MatCardModule } from '@angular/material/card';
import { MatFormFieldModule } from '@angular/material/form-field';
import { MatAutocompleteModule } from '@angular/material/autocomplete';
import { MatProgressSpinnerModule } from '@angular/material/progress-spinner';
import { MatCheckboxModule } from '@angular/material/checkbox';
import { MatTableModule } from '@angular/material/table';
import { MatMenuModule } from '@angular/material/menu';
import { FileUploadComponent } from '@app/components/file-upload/file-upload.component';
import { SearchComponent } from '@app/components/search/search.component';
import { DocumentStatusComponent } from '@app/components/document-status/document-status.component';
import { SearchService } from './services/search.service';
@NgModule({
declarations: [
AppComponent,
SearchComponent,
FileUploadComponent,
DocumentStatusComponent
],
imports: [
BrowserModule,
HttpClientModule,
AppRoutingModule,
BrowserAnimationsModule,
ReactiveFormsModule,
FormsModule,
FlexLayoutModule,
MatInputModule,
MatCardModule,
MatFormFieldModule,
MatAutocompleteModule,
MatDialogModule,
MatProgressSpinnerModule,
MatButtonModule,
MatIconModule,
MatChipsModule,
MatCheckboxModule,
MatTableModule,
MatMenuModule
],
providers: [
SearchService
],
bootstrap: [AppComponent]
})
export class AppModule { }
Backend
So let's now get to the Backend!
Overview
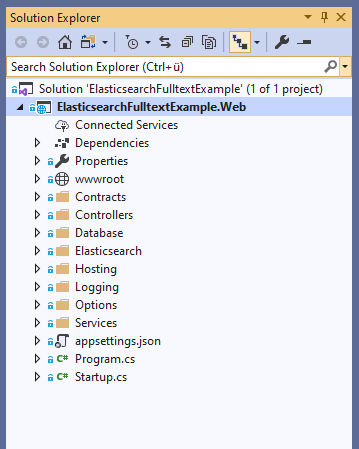
It's a good idea to look at the high-level structure of the Backend first:
These namespaces are used for:
Contracts- The Data Transfer Objects exchanged between the Frontend and Backend.
Controllers- The API Endpoints the Frontend queries for Suggestions and Search results.
Database- The uploaded documents and the meta data are directly stored in a Relational database.
Elasticsearch- The Elasticsearch integration layer, which includes creating the Index, Pipelines and so on.
Hosting- We need to run Background Services for preparing the SQL database, creating the Elasticsearch index and pipeline and running a loop to index documents.
Logging- Abstractions for the Microsoft
ILoggerinterfaces.
- Abstractions for the Microsoft
Options- There are many options we can set for the application. Think of:
- Elasticsearch index name or port
- SQL Database Connection String
- Tesseract parameters
- ...
- The idea is to use the ASP.NET Core functionality for reading options from the configuration.
- There are many options we can set for the application. Think of:
Services- The Application Services for:
- Indexing documents in Elasticsearch
- Runnung OCR on a document using Tesseract
- The Application Services for:
Programs.cs- Defines the Webservers directories, ports and so on.
Startup.cs- Configures the HTTP Pipeline.
Now documenting and explaining how code fits together is always somewhat complicated.
And I am particularly bad at UML Class Diagrams and UML Sequence Diagrams.
So I explain it in a way it makes sense to me.
Database
Let's start with the database.
Document databases are perfect for what they are meant to be: Indexing document and providing a fulltext search engines. It's not useful to shoehorn a Document database like Elasticsearch into the single source of truth. That's what I am always using Postgres for.
It works like this: I will write the file and meta data into a Postgres database first. "What the actual ...! You cannot write binary data into a SQL database!" I hear you say. But it's like this: Keeping files on disk and database in sync requires a complexity I don't want to introduce in a simple example.
And while you are not scaling to thousands of concurrent users: Keep It Simple, Stupid.
Plus modern databases come with features, that allow storing large binary files in rows without performance impact:
Project Structure
It's good to get an Overview first, how the Database namespace is structured.
Context- Holds the Entity Framework
DbContext.
- Holds the Entity Framework
Factory- A Factory to create a
DbContextwhen needed, instead of injecting a scopedDbContext.
- A Factory to create a
Migrations- Database Migrations for creating and updating the database schema.
Model- The object model representing the database.
TypeConfigurations- The mapping between the database model and object model-
ValueComparers- For Snapshotting and Value comparisms it's sometimes needed to define a
ValueComparer.
- For Snapshotting and Value comparisms it's sometimes needed to define a
ValueConverters- Sometimes the database model and the object model doesn't match, and representations need to be converted.
So it starts with the Model, that define what a Document in the database looks like:
using System;
namespace ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web.Database.Model
{
public class Document
{
/// <summary>
/// A unique document id.
/// </summary>
public int Id { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// The Title of the Document for Suggestion.
/// </summary>
public string Title { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// The Original Filename of the uploaded document.
/// </summary>
public string Filename { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// The Data of the Document.
/// </summary>
public byte[] Data { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Keywords to filter for.
/// </summary>
public string[] Keywords { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Suggestions for the Autocomplete Field.
/// </summary>
public string[] Suggestions { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// OCR Data.
/// </summary>
public bool IsOcrRequested { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// The Date the Document was uploaded.
/// </summary>
public DateTime UploadedAt { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// The Date the Document was indexed at.
/// </summary>
public DateTime? IndexedAt { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// The Document Status.
/// </summary>
public StatusEnum Status { get; set; }
}
}
The Status of the Document is defined in the StatusEnum and it maps to the one defined in the Contracts:
namespace ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web.Database.Model
{
/// <summary>
/// Defines all possible states a document can have.
/// </summary>
public enum StatusEnum
{
/// <summary>
/// The document has no Status assigned.
/// </summary>
None = 0,
/// <summary>
/// The document is scheduled for indexing by a BackgroundService.
/// </summary>
ScheduledIndex = 1,
/// <summary>
/// The document is scheduled for deletion by a BackgroundService.
/// </summary>
ScheduledDelete = 2,
/// <summary>
/// The document has been indexed.
/// </summary>
Indexed = 3,
/// <summary>
/// The document indexing has failed due to an error.
/// </summary>
Failed = 4,
/// <summary>
/// The document has been removed from the index.
/// </summary>
Deleted = 5
}
}
Mapping to Database Table and Columns
EntityFramework Core provides the interface IEntityTypeConfiguration<T> to build mappings between the
database schema and the object model. I always prefer to use an IEntityTypeConfiguration<T>, instead of
using Attributes.
using ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web.Database.Model;
using ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web.Database.ValueComparers;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Metadata.Builders;
namespace ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web.Database.TypeConfigurations
{
public class DocumentTypeConfiguration : IEntityTypeConfiguration<Document>
{
public void Configure(EntityTypeBuilder<Document> builder)
{
builder
.ToTable("documents")
.HasKey(x => x.Id);
builder
.Property(x => x.Id)
.HasColumnName("id")
.ValueGeneratedOnAdd();
builder
.Property(x => x.Filename)
.HasColumnName("filename")
.IsRequired();
builder
.Property(x => x.Title)
.HasColumnName("title")
.IsRequired();
builder
.Property(x => x.Data)
.HasColumnName("data")
.IsRequired();
builder
.Property(x => x.Suggestions)
.HasColumnName("suggestions")
.HasConversion(new DelimitedStringValueConverter(','))
.IsRequired()
.Metadata.SetValueComparer(new StringArrayValueComparer());
builder
.Property(x => x.Keywords)
.HasColumnName("keywords")
.HasConversion(new DelimitedStringValueConverter(','))
.IsRequired()
.Metadata.SetValueComparer(new StringArrayValueComparer());
builder
.Property(x => x.IsOcrRequested)
.HasColumnName("is_ocr_requested")
.IsRequired();
builder
.Property(x => x.UploadedAt)
.HasColumnName("uploaded_at")
.IsRequired();
builder
.Property(x => x.IndexedAt)
.HasColumnName("indexed_at");
builder
.Property(x => x.Status)
.HasColumnName("status")
.HasConversion<int>()
.IsRequired();
}
}
}
There are a few things to note.
- The
StatusEnumis converted to anint, when writing to the database and converted fromintto theStatusEnumon its way back. KeywordsandSuggestionsare just comma separated lists. If you need to query for keywords or suggestions create tables for them.
Converting between a String[] and String
You could easily switch the database for this example from let's say PostgreSQL to SQLite. And while Postgres knows how to deal with arrays, SQLite or other databases do not. That's why we just write a comma separated list when writing the array, and split the data on reading it back from the database.
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Storage.ValueConversion;
using System.Linq;
using TinyCsvParser.Tokenizer;
namespace ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web.Database
{
public class DelimitedStringValueConverter : ValueConverter<string[], string>
{
public DelimitedStringValueConverter(char delimiter)
: this(delimiter, new QuotedStringTokenizer(delimiter))
{
}
public DelimitedStringValueConverter(char delimiter, ITokenizer tokenizer)
: base(x => BuildDelimitedLine(x, delimiter), x => tokenizer.Tokenize(x), null)
{
}
private static string BuildDelimitedLine(string[] values, char delimiter)
{
var quotedValues = values.Select(value => $"\"{value}\"");
return string.Join(delimiter, quotedValues);
}
}
}
EntityFramework Core needs something called a ValueComparer<T> when operating on the ChangeTracking graph, because it needs to know
if a value has changed and its update magic should be applied. So we are providing a StringArrayValueComparer:
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.ChangeTracking;
using System;
using System.Linq;
namespace ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web.Database.ValueComparers
{
public class StringArrayValueComparer : ValueComparer<string[]>
{
public StringArrayValueComparer()
: base((c1, c2) => c1.SequenceEqual(c2), c => c.Aggregate(0, (a, v) => HashCode.Combine(a, v.GetHashCode())), c => c.ToArray()) { }
}
}
The DbContext
The ApplicationDbContext now has one DbSet<Document>. We are using the EntityFramework Core Fluent mappings, so it's neccessary
to override the OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder) method and pass the IEntityTypeConfiguration.
using ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web.Database.Model;
using ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web.Database.TypeConfigurations;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web.Database.Context
{
public class ApplicationDbContext : DbContext
{
public ApplicationDbContext(DbContextOptions options)
: base(options) { }
public DbSet<Document> Documents { get; set; }
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
modelBuilder.ApplyConfiguration(new DocumentTypeConfiguration());
}
}
}
Reasons behind a DbContextFactory
You may have seen, that I a factory is used to create a new DbContext. Why on earth is he doing this you might ask?
In EntityFramework 6 it was possible to simply instantiate a DbContext when you felt like:
using(var context = new ApplicationDbContext("MyConnectionString")
{
// ...
}
But in ASP.NET Core you are supposed to inject the DbContext and there is no obvious way to pass a Connection String
from a configuration file into the DbContext. The EntityFramework Core issue tracker on GitHub contains an interesting
discussion on this:
And while there are probably some ways of fixing this, I simply add another abstraction layer and have a factory building
the DbContext for me. This way I don't have to deal with injecting a DbContext and don't have to think about it's scope,
lifetime and the state of the ChangeTracker.
using ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web.Database.Context;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web.Database.Factory
{
public class ApplicationDbContextFactory
{
private readonly DbContextOptions options;
public ApplicationDbContextFactory(DbContextOptions options)
{
this.options = options;
}
public ApplicationDbContext Create()
{
return new ApplicationDbContext(options);
}
}
}
Creating the DB Migrations
By installing Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Tools I can create and apply Database migrations directly from the Package Manager console.
I want the Migrations to go to Database/Migrations of the Project, so I am creating the InitialMigration to create the table like this:
Add-Migration InitialCreate -Context ApplicationDbContext -OutputDir "Database/Migrations"
And that's it for the database side.
Tesseract for Optical Character Recognition
To extract text from images and make it indexable we employ Tesseract, which is one of the most popular free OCR engines.
What's OCR? According to Wikipedia ...
Optical character recognition or optical character reader (OCR) is the electronic or mechanical conversion of images of typed, handwritten or printed text into machine-encoded text, whether from a scanned document, a photo of a document, a scene-photo (for example the text on signs and billboards in a landscape photo) or from subtitle text superimposed on an image (for example from a television broadcast).
And what is Tesseract? Again according to Wikipedia ...
Tesseract is an optical character recognition engine for various operating systems. It is free software, released under the Apache License. Originally developed by Hewlett-Packard as proprietary software in the 1980s, it was released as open source in 2005 and development has been sponsored by Google since 2006.
In 2006, Tesseract was considered one of the most accurate open-source OCR engines then available.
And how can we use it in Windows? Fortunately we don't need to build it ourselves from source. The UB Mannheim provides pre-built windows executables for the latest Tesseract releases, that we can use:
.NET Implementation for Tesseract OCR
When looking at how to use Tesseract I found some .NET libraries, that wrapped the DLLs. But most of them were either outdated or way to complicated to use. For the example article, I just want to extract english text using the default parameters.
So what I do: Instead of going low-level I kick off a System.Diagnostics.Process, that writes the OCR results into a
temporary text file and deletes it after the recognition is done. Does it scale? Most probably not. But again: We are indexing
the documents as Background jobs anyway it is important for me, that no magic is involved.
using ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web.Logging;
using ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web.Options;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Options;
using System;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.IO;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web.Services
{
public class TesseractService
{
private readonly ILogger<TesseractService> logger;
private readonly TesseractOptions tesseractOptions;
public TesseractService(ILogger<TesseractService> logger, IOptions<TesseractOptions> tesseractOptions)
{
this.logger = logger;
this.tesseractOptions = tesseractOptions.Value;
}
public async Task<string> ProcessDocument(byte[] document, string language)
{
var temporarySourceFilename = Path.Combine(tesseractOptions.TempDirectory, Path.GetRandomFileName());
var temporaryTargetFilename = Path.Combine(tesseractOptions.TempDirectory, Path.GetRandomFileName());
if (logger.IsInformationEnabled())
{
logger.LogInformation($"Generating Temporary Filenames (Source = \"{temporarySourceFilename}\", Target = \"{temporaryTargetFilename}\")");
}
// The Tesseract CLI in 5.0.0-alpha always adds a .txt to the output file:
var temporaryTesseractOutputFile = $"{temporaryTargetFilename}.txt";
try
{
await File.WriteAllBytesAsync(temporarySourceFilename, document);
var tesseractArguments = $"{temporarySourceFilename} {temporaryTargetFilename} -l {language}";
if(logger.IsInformationEnabled())
{
logger.LogInformation($"Running OCR Command: \"{tesseractOptions.Executable} {tesseractArguments}\"");
}
var result = await RunProcessAsync(tesseractOptions.Executable, tesseractArguments);
if (result != 0)
{
if (logger.IsErrorEnabled())
{
logger.LogError($"Tesseract Exited with Error Code = \"{result}\"");
}
throw new Exception($"Tesseract exited with Error Code \"{result}\"");
}
if (!File.Exists(temporaryTesseractOutputFile))
{
if(logger.IsWarningEnabled())
{
logger.LogWarning("Tesseract failed to extract data from the document. No output document exists.");
}
return string.Empty;
}
var ocrDocumentText = File.ReadAllText(temporaryTesseractOutputFile);
if (logger.IsDebugEnabled())
{
logger.LogDebug($"Tesseract extracted the following text from the document: {ocrDocumentText}");
}
return ocrDocumentText;
}
finally
{
if (logger.IsDebugEnabled())
{
logger.LogDebug($"Deleting temporary files (Source = \"{temporarySourceFilename}\", Target = \"{temporaryTargetFilename}\")");
}
if (File.Exists(temporarySourceFilename))
{
File.Delete(temporarySourceFilename);
}
if (File.Exists(temporaryTesseractOutputFile))
{
File.Delete(temporaryTesseractOutputFile);
}
}
}
private Task<int> RunProcessAsync(string filename, string arguments)
{
if(logger.IsDebugEnabled())
{
logger.LogDebug($"Running Process Asynchronously: Filename = {filename}, Arguments = {arguments}");
}
var tcs = new TaskCompletionSource<int>();
var process = new Process
{
StartInfo = { FileName = filename, Arguments = arguments },
EnableRaisingEvents = true
};
process.Exited += (sender, args) =>
{
tcs.SetResult(process.ExitCode);
process.Dispose();
};
process.Start();
return tcs.Task;
}
}
}
Elasticsearch
If you are working with .NET there is a great library to interface with an Elasticsearch server: NEST.
According to the Elasticsearch documentation NEST ...
... is a high level client that maps all requests and responses as types, and comes with a strongly typed query DSL that maps 1 to 1 with the Elasticsearch query DSL. It takes advantage of specific .NET features to provide higher level abstractions such as auto mapping of CLR types. Internally, NEST uses and still exposes the low level Elasticsearch.Net client, providing access to the power of NEST and allowing users to drop down to the low level client when wishing to.
Elasticsearch can be extended using Plugins, which brings us back to the original question: "How do we read data from Excel, Powerpoint, PDF, ... files?". And finally we can answer it. In this example it's done by using the Ingest Attachment Processor Plugin:
The ingest attachment plugin lets Elasticsearch extract file attachments in common formats (such as PPT, XLS, and PDF) by using the Apache text extraction library Tika.
You can use the ingest attachment plugin as a replacement for the mapper attachment plugin.
The source field must be a base64 encoded binary. If you do not want to incur the overhead of converting back and forth between base64, you can use the CBOR format instead of JSON and specify the field as a bytes array instead of a string representation. The processor will skip the base64 decoding then.
Most of the code in this article is taken from "The Future of Attachments for Elasticsearch and .NET":
ElasticsearchDocument
What should the document in Elasticsearch look like? This is defined in the ElasticsearchDocument class.
I suggest reading the "The Future of Attachments for Elasticsearch and .NET" for more information:
The ElasticsearchDocument model now looks like this:
using Nest;
using System;
namespace ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web.Elasticsearch.Model
{
public class ElasticsearchDocument
{
/// <summary>
/// A unique document id.
/// </summary>
public string Id { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// The Title of the Document for Suggestion.
/// </summary>
public string Title { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// The Original Filename of the uploaded document.
/// </summary>
public string Filename { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// The Data of the Document.
/// </summary>
public byte[] Data { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Keywords to filter for.
/// </summary>
public string[] Keywords { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Suggestions for the Autocomplete Field.
/// </summary>
public string[] Suggestions { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// The Date the document was indexed on.
/// </summary>
public DateTime IndexedOn { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// OCR Data.
/// </summary>
public string Ocr { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// The Attachment.
/// </summary>
public Attachment Attachment { get; set; }
}
}
Create the Elasticsearch mapping using the Mapping API
The ElasticsearchDocument Mapping is defined in the method ElasticsearchClient#CreateIndexAsync. Again most of the Attachment
mapping was taken from the elastic.co blog post. We are mapping the Keywords property to a Keyword field type and the
Suggestions will be mapped with a Completion field type.
using Elasticsearch.Net;
using ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web.Elasticsearch.Model;
using ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web.Logging;
using ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web.Options;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Options;
using Nest;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web.Elasticsearch
{
public class ElasticsearchClient
{
private readonly ILogger<ElasticsearchClient> logger;
private readonly IElasticClient client;
private readonly string indexName;
public ElasticsearchClient(ILogger<ElasticsearchClient> logger, IOptions<ElasticsearchOptions> options)
: this(logger, CreateClient(options.Value.Uri), options.Value.IndexName)
{
}
public ElasticsearchClient(ILogger<ElasticsearchClient> logger, IElasticClient client, string indexName)
{
this.logger = logger;
this.indexName = indexName;
this.client = client;
}
public async Task<CreateIndexResponse> CreateIndexAsync(CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
var createIndexResponse = await client.Indices.CreateAsync(indexName, descriptor =>
{
return descriptor.Map<ElasticsearchDocument>(mapping => mapping
.Properties(properties => properties
.Text(textField => textField.Name(document => document.Id))
.Text(textField => textField.Name(document => document.Title))
.Text(textField => textField.Name(document => document.Filename))
.Text(textField => textField.Name(document => document.Ocr))
.Binary(textField => textField.Name(document => document.Data))
.Date(dateField => dateField.Name(document => document.IndexedOn))
.Keyword(keywordField => keywordField.Name(document => document.Keywords))
.Completion(completionField => completionField.Name(document => document.Suggestions))
.Object<Attachment>(attachment => attachment
.Name(document => document.Attachment)
.Properties(attachmentProperties => attachmentProperties
.Text(t => t.Name(n => n.Name))
.Text(t => t.Name(n => n.Content))
.Text(t => t.Name(n => n.ContentType))
.Number(n => n.Name(nn => nn.ContentLength))
.Date(d => d.Name(n => n.Date))
.Text(t => t.Name(n => n.Author))
.Text(t => t.Name(n => n.Title))
.Text(t => t.Name(n => n.Keywords))))));
}, cancellationToken);
if (logger.IsDebugEnabled())
{
logger.LogDebug($"CreateIndexResponse DebugInformation: {createIndexResponse.DebugInformation}");
}
return createIndexResponse;
}
}
}
Creating the Attachments Pipeline
The Attachments Pipeline in Elasticsearch is configured using the Pipeline API. We are using the Data Field as
source for the Attachment target field. The Ingest Attachment Processor Plugin then knows, that it should use
the Data field to populate the Attachment.
Once we are done, we are removing the data Field from the document index, so we do not pollute the cluster with
huge Base64 content, that is also stored in the Database.
namespace ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web.Elasticsearch
{
public class ElasticsearchClient
{
// ...
public async Task<PutPipelineResponse> CreatePipelineAsync(CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
var putPipelineResponse = await client.Ingest.PutPipelineAsync("attachments", p => p
.Description("Document attachment pipeline")
.Processors(pr => pr
.Attachment<ElasticsearchDocument>(a => a
.Field(f => f.Data)
.TargetField(f => f.Attachment))
.Remove<ElasticsearchDocument>(x => x.Field("data"))), cancellationToken);
if (logger.IsDebugEnabled())
{
logger.LogDebug($"PutPipelineResponse DebugInformation: {putPipelineResponse.DebugInformation}");
}
return putPipelineResponse;
}
}
}
Providing Suggestions
To Provide Suggestions to a user we can use the Suggest API. I am using the input query as a Prefix, so if you type
"Data M" you will get "Data Mining" and not some infix suggestion like "... a book about Data Mining ....
We are also skipping all duplicates, because it's not useful to provide duplicates in an Auto-Completion Box on
client-side and finally use "suggest" as the key for suggestions, when we get the Search Response back.
namespace ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web.Elasticsearch
{
public class ElasticsearchClient
{
// ...
public Task<ISearchResponse<ElasticsearchDocument>> SuggestAsync(string query, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
return client.SearchAsync<ElasticsearchDocument>(x => x
// Query this Index:
.Index(indexName)
// Suggest Titles:
.Suggest(s => s
.Completion("suggest", x => x
.Prefix(query)
.SkipDuplicates(true)
.Field(x => x.Suggestions))), cancellationToken);
}
}
}
Executing the Search
For the queries we are using the Elasticsearch Search API. We are running the query as a MultiMatch query of
type BoolPrefix. We are searching over the indexed fields Keywords, Ocr and the Attachments content
in Attachment.Content.
To highlight the results we are using the Elasticsearch Highlighter API. Actually we are already using the HTML Tag
<strong> to highlight the results. This HTML will be directly sent back to the client, so you now probably understand
why the Angular Components are using an innerHtml directive.
namespace ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web.Elasticsearch
{
public class ElasticsearchClient
{
// ...
public Task<ISearchResponse<ElasticsearchDocument>> SearchAsync(string query, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
return client.SearchAsync<ElasticsearchDocument>(document => document
// Query this Index:
.Index(indexName)
// Highlight Text Content:
.Highlight(highlight => highlight
.Fields(
fields => fields
.Fragmenter(HighlighterFragmenter.Span)
.PreTags("<strong>")
.PostTags("</strong>")
.FragmentSize(150)
.NoMatchSize(150)
.NumberOfFragments(5)
.Field(x => x.Ocr),
fields => fields
.Fragmenter(HighlighterFragmenter.Span)
.PreTags("<strong>")
.PostTags("</strong>")
.FragmentSize(150)
.NoMatchSize(150)
.NumberOfFragments(5)
.Field(x => x.Attachment.Content))
)
// Now kick off the query:
.Query(q => q.MultiMatch(mm => mm
.Query(query)
.Type(TextQueryType.BoolPrefix)
.Fields(f => f
.Field(d => d.Keywords)
.Field(d => d.Ocr)
.Field(d => d.Attachment.Content)))), cancellationToken);
}
}
}
Running Tesseract OCR before Indexing the Document
We are using Tesseract OCR to extract data from an image or document. So before adding a document to Elasticsearch it
might be neccessary to apply the OCR step, which is done in yet another service we define, the
ElasticsearchIndexService.
using ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web.Database.Model;
using ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web.Elasticsearch;
using ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web.Elasticsearch.Model;
using ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web.Logging;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
using Nest;
using System;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web.Services
{
public class ElasticsearchIndexService
{
private readonly ILogger<ElasticsearchIndexService> logger;
private readonly TesseractService tesseractService;
private readonly ElasticsearchClient elasticsearchClient;
public ElasticsearchIndexService(ILogger<ElasticsearchIndexService> logger, ElasticsearchClient elasticsearchClient, TesseractService tesseractService)
{
this.logger = logger;
this.elasticsearchClient = elasticsearchClient;
this.tesseractService = tesseractService;
}
public async Task<IndexResponse> IndexDocumentAsync(Document document, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
return await elasticsearchClient.IndexAsync(new ElasticsearchDocument
{
Id = document.Id.ToString(),
Title = document.Title,
Filename = document.Filename,
Suggestions = document.Suggestions,
Keywords = document.Suggestions,
Data = document.Data,
Ocr = await GetOcrDataAsync(document),
IndexedOn = DateTime.UtcNow,
}, cancellationToken);
}
public async Task<DeleteResponse> DeleteDocumentAsync(Document document, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
return await elasticsearchClient.DeleteAsync(document.Id.ToString(), cancellationToken);
}
public async Task<PingResponse> PingAsync(CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
return await elasticsearchClient.PingAsync(cancellationToken: cancellationToken);
}
private async Task<string> GetOcrDataAsync(Document document)
{
if(!document.IsOcrRequested)
{
if(logger.IsDebugEnabled())
{
logger.LogDebug($"OCR Processing not requested for Document ID '{document.Id}'");
}
return string.Empty;
}
if (logger.IsDebugEnabled())
{
logger.LogDebug($"Running OCR for Document ID '{document.Id}'");
}
return await tesseractService
.ProcessDocument(document.Data, "eng")
.ConfigureAwait(false);
}
}
}
Connecting all the things
IndexController
In the Frontend section we have seen, that I am using a multipart/form-data request to upload documents and meta data.
Data Model
In the Contract namespace we define the DocumentUploadDto, that the request binds to. Binding Form data is done by using [FromForm]
attributes and for the file we can use an IFormFile, which is coming with ASP.NET Core framework. The underlying Model Binder in ASP.NET
Core knows how to handle all this.
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
namespace ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web.Contracts
{
public class DocumentUploadDto
{
[FromForm(Name = "title")]
public string Title { get; set; }
[FromForm(Name = "suggestions")]
public string Suggestions { get; set; }
[FromForm(Name = "isOcrRequested")]
public string IsOcrRequested { get; set; }
[FromForm(Name = "file")]
public IFormFile File { get; set; }
}
}
Controller
The Controller receives the DocumentUploadDto and schedules the file for indexing.
The IndexController has one Endpoint /api/index, which binds the DocumentUploadDto passed as Form data. I want
everything to be asynchronous from the start, so the method also gets a CancellationToken passed into. The
CancellationToken is automatically set by the ASP.NET Core environment.
The Controller gets two dependencies injected:
ILogger<IndexController>the MicrosoftILoggerabstraction for Logging.ApplicationDbContextFactorya factory to create aDbContextfor writing to the database.
The Keywords are passed as a comma separated list, so when receiving the data we tokenize the values.
using ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web.Contracts;
using ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web.Database.Factory;
using ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web.Database.Model;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using TinyCsvParser.Tokenizer;
using ITokenizer = TinyCsvParser.Tokenizer.ITokenizer;
namespace ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web.Controllers
{
public class IndexController : Controller
{
private readonly ILogger<IndexController> logger;
private readonly ITokenizer suggestionsTokenizer;
private readonly ApplicationDbContextFactory applicationDbContextFactory;
public IndexController(ILogger<IndexController> logger, ApplicationDbContextFactory applicationDbContextFactory)
{
this.logger = logger;
this.suggestionsTokenizer = new QuotedStringTokenizer(',');
this.applicationDbContextFactory = applicationDbContextFactory;
}
[HttpPost]
[Route("/api/index")]
public async Task<IActionResult> IndexDocument([FromForm] DocumentUploadDto documentDto, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
try
{
await ScheduleIndexing(documentDto, cancellationToken);
return Ok();
}
catch (Exception e)
{
logger.LogError(e, "Failed to schedule document for Indexing");
return StatusCode(500);
}
}
private async Task ScheduleIndexing(DocumentUploadDto documentDto, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
using (var context = applicationDbContextFactory.Create())
{
using (var transaction = await context.Database.BeginTransactionAsync())
{
bool.TryParse(documentDto.IsOcrRequested, out var isOcrRequest);
var document = new Document
{
Title = documentDto.Title,
Filename = documentDto.File.FileName,
Suggestions = GetSuggestions(documentDto.Suggestions),
Keywords = GetSuggestions(documentDto.Suggestions),
Data = await GetBytesAsync(documentDto.File),
IsOcrRequested = isOcrRequest,
UploadedAt = DateTime.UtcNow,
Status = StatusEnum.ScheduledIndex
};
context.Documents.Add(document);
await context.SaveChangesAsync(cancellationToken);
await transaction.CommitAsync();
}
}
}
private string[] GetSuggestions(string suggestions)
{
if (suggestions == null)
{
return null;
}
return suggestionsTokenizer
.Tokenize(suggestions)
.Select(x => x.Trim())
.ToArray();
}
private async Task<byte[]> GetBytesAsync(IFormFile formFile)
{
using (var memoryStream = new MemoryStream())
{
await formFile.CopyToAsync(memoryStream);
return memoryStream.ToArray();
}
}
}
}
So all the Controller does is writing the turning a DocumentUploadDto into a Database.Model.Document and then write it into the PostgreSQL database.
What's the deal with the ScheduledIndex Status? See there may come times when a Server is under high contention and a single server won't be able to index
and process incoming files. The actual indexing to Elasticsearch might be a time-intensive and resource-intensive job, that probably takes some seconds. It's
probably enough for a user to know: My document has been successfully uploaded and will be indexed in a minute.
DocumentIndexer BackgroundService
So who does actually index the documents? This is done by using an ASP.NET Core BackgroundService, which periodically:
- Gets Documents in Status
ScheduledIndex - Index the Document to Elasticsearch and run Tesseract OCR
... and ...
- Gets the Document in Status
ScheduledDelete - Deletes the Document from Elasticsearch
All of this should be done in a Database Transaction, so even if you have multiple consumers we wouldn't index or delete a document twice.
using ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web.Database.Factory;
using ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web.Database.Model;
using ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web.Logging;
using ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web.Options;
using ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web.Services;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Options;
using System;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web.Hosting
{
public class DocumentIndexerHostedService : BackgroundService
{
private readonly IndexerOptions options;
private readonly ILogger<DocumentIndexerHostedService> logger;
private readonly ApplicationDbContextFactory applicationDbContextFactory;
private readonly ElasticsearchIndexService elasticsearchIndexService;
public DocumentIndexerHostedService(ILogger<DocumentIndexerHostedService> logger, IOptions<IndexerOptions> options, ApplicationDbContextFactory applicationDbContextFactory, ElasticsearchIndexService elasticsearchIndexService)
{
this.logger = logger;
this.options = options.Value;
this.elasticsearchIndexService = elasticsearchIndexService;
this.applicationDbContextFactory = applicationDbContextFactory;
}
protected override async Task ExecuteAsync(CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
var indexDelay = TimeSpan.FromSeconds(options.IndexDelay);
if (logger.IsDebugEnabled())
{
logger.LogDebug($"DocumentIndexer is starting with Index Delay: {options.IndexDelay} seconds.");
}
cancellationToken.Register(() => logger.LogDebug($"DocumentIndexer background task is stopping."));
while (!cancellationToken.IsCancellationRequested)
{
if (logger.IsDebugEnabled())
{
logger.LogDebug($"DocumentIndexer is running indexing loop.");
}
try
{
await IndexDocumentsAsync(cancellationToken);
}
catch(Exception e)
{
logger.LogError(e, "Indexing failed due to an Exception");
}
await Task.Delay(indexDelay, cancellationToken);
}
logger.LogDebug($"DocumentIndexer exited the Index Loop.");
}
private async Task IndexDocumentsAsync(CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
await IndexScheduledDocuments(cancellationToken);
await RemoveDeletedDocuments(cancellationToken);
async Task RemoveDeletedDocuments(CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
using (var context = applicationDbContextFactory.Create())
{
using (var transaction = await context.Database.BeginTransactionAsync())
{
var documents = await context.Documents
.Where(x => x.Status == StatusEnum.ScheduledDelete)
.AsNoTracking()
.ToListAsync(cancellationToken);
foreach (Document document in documents)
{
if (logger.IsInformationEnabled())
{
logger.LogInformation($"Removing Document: {document.Id}");
}
try
{
var deleteDocumentResponse = await elasticsearchIndexService.DeleteDocumentAsync(document, cancellationToken);
if (deleteDocumentResponse.IsValid)
{
await context.Database.ExecuteSqlInterpolatedAsync($"UPDATE documents SET status = {StatusEnum.Deleted}, indexed_at = {null} where id = {document.Id}");
}
else
{
await context.Database.ExecuteSqlInterpolatedAsync($"UPDATE documents SET status = {StatusEnum.Failed} where id = {document.Id}");
}
}
catch (Exception e)
{
logger.LogError(e, $"Removing Document '{document.Id}' failed");
await context.Database.ExecuteSqlInterpolatedAsync($"UPDATE documents SET status = {StatusEnum.Failed} where id = {document.Id}");
}
if (logger.IsInformationEnabled())
{
logger.LogInformation($"Finished Removing Document: {document.Id}");
}
}
await transaction.CommitAsync();
}
}
}
async Task IndexScheduledDocuments(CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
using (var context = applicationDbContextFactory.Create())
{
using (var transaction = await context.Database.BeginTransactionAsync())
{
var documents = await context.Documents
.Where(x => x.Status == StatusEnum.ScheduledIndex)
.AsNoTracking()
.ToListAsync(cancellationToken);
foreach (Document document in documents)
{
if (logger.IsInformationEnabled())
{
logger.LogInformation($"Start indexing Document: {document.Id}");
}
try
{
var indexDocumentResponse = await elasticsearchIndexService.IndexDocumentAsync(document, cancellationToken);
if (indexDocumentResponse.IsValid)
{
await context.Database.ExecuteSqlInterpolatedAsync($"UPDATE documents SET status = {StatusEnum.Indexed}, indexed_at = {DateTime.UtcNow} where id = {document.Id}");
}
else
{
await context.Database.ExecuteSqlInterpolatedAsync($"UPDATE documents SET status = {StatusEnum.Failed}, indexed_at = {null} where id = {document.Id}");
}
}
catch (Exception e)
{
logger.LogError(e, $"Indexing Document '{document.Id}' failed");
await context.Database.ExecuteSqlInterpolatedAsync($"UPDATE documents SET status = {StatusEnum.Failed}, indexed_at = {null} where id = {document.Id}");
}
if (logger.IsInformationEnabled())
{
logger.LogInformation($"Finished indexing Document: {document.Id}");
}
}
await transaction.CommitAsync();
}
}
}
}
}
}
SearchController
The SearchController provides the API Endpoints:
/api/searchfor Fulltext Search Queries/api/suggestfor getting Search Suggestions
There is a little complication in the code. I didn't find a simple way to automatically highlight the Prefix part of a suggestion
when using a Completion field type in Elasticsearch. There might be ways to do it, but even digging through the Nest code
didn't help.
The Rest of the code is some data conversion between the Webservice representation and the Elasticsearch representation of a Search Result. I didn't invest too much time in writing abstractions around the code, because it is the only place we need it.
using ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web.Contracts;
using ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web.Elasticsearch;
using ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web.Options;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Options;
using Nest;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web.Controllers
{
public class SearchController : Controller
{
private readonly ApplicationOptions applicationOptions;
private readonly ElasticsearchClient elasticsearchClient;
public SearchController(IOptions<ApplicationOptions> applicationOptions, ElasticsearchClient elasticsearchClient)
{
this.applicationOptions = applicationOptions.Value;
this.elasticsearchClient = elasticsearchClient;
}
[HttpGet]
[Route("/api/search")]
public async Task<IActionResult> Query([FromQuery(Name = "q")] string query, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
var searchResponse = await elasticsearchClient.SearchAsync(query, cancellationToken);
var searchResult = ConvertToSearchResults(query, searchResponse);
return Ok(searchResult);
}
[HttpGet]
[Route("/api/suggest")]
public async Task<IActionResult> Suggest([FromQuery(Name = "q")] string query, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
var searchResponse = await elasticsearchClient.SuggestAsync(query, cancellationToken);
var searchSuggestions = ConvertToSearchSuggestions(query, searchResponse);
return Ok(searchSuggestions);
}
private SearchSuggestionsDto ConvertToSearchSuggestions(string query, ISearchResponse<Elasticsearch.Model.ElasticsearchDocument> searchResponse)
{
return new SearchSuggestionsDto
{
Query = query,
Results = GetSuggestions(searchResponse)
};
}
private SearchSuggestionDto[] GetSuggestions(ISearchResponse<Elasticsearch.Model.ElasticsearchDocument> searchResponse)
{
if (searchResponse == null)
{
return null;
}
var suggest = searchResponse.Suggest;
if (suggest == null)
{
return null;
}
if(!suggest.ContainsKey("suggest"))
{
return null;
}
var suggestions = suggest["suggest"];
if (suggestions == null)
{
return null;
}
// What we are doing here...? The Complete Field Type has no simple
// way to highlight the matched Prefix / Infix. We are instead replacing
// the matched completions:
var result = new List<SearchSuggestionDto>();
foreach (var suggestion in suggestions)
{
var offset = suggestion.Offset;
var length = suggestion.Length;
foreach (var option in suggestion.Options)
{
var text = option.Text;
var prefix = option.Text.Substring(offset, Math.Min(length, text.Length));
var highlight = ReplaceAt(option.Text, offset, length, $"<strong>{prefix}</strong>");
result.Add(new SearchSuggestionDto { Text = text, Highlight = highlight });
}
}
return result.ToArray();
}
public static string ReplaceAt(string str, int index, int length, string replace)
{
return str
.Remove(index, Math.Min(length, str.Length - index))
.Insert(index, replace);
}
private SearchResultsDto ConvertToSearchResults(string query, ISearchResponse<Elasticsearch.Model.ElasticsearchDocument> searchResponse)
{
var searchResults = searchResponse
// Get the Hits:
.Hits
// Convert the Hit into a SearchResultDto:
.Select(x => new SearchResultDto
{
Identifier = x.Source.Id,
Title = x.Source.Title,
Keywords = x.Source.Keywords,
Matches = GetMatches(x.Highlight),
Url = $"{applicationOptions.BaseUri}/api/files/{x.Source.Id}"
})
// And convert to array:
.ToArray();
return new SearchResultsDto
{
Query = query,
Results = searchResults
};
}
private string[] GetMatches(IReadOnlyDictionary<string, IReadOnlyCollection<string>> highlight)
{
var matchesForOcr = GetMatchesForField(highlight, "ocr");
var matchesForContent = GetMatchesForField(highlight, "attachment.content");
return Enumerable
.Concat(matchesForOcr, matchesForContent)
.ToArray();
}
private string[] GetMatchesForField(IReadOnlyDictionary<string, IReadOnlyCollection<string>> highlight, string field)
{
if(highlight == null)
{
return new string[] { };
}
if(highlight.TryGetValue(field, out var matches))
{
return matches.ToArray();
}
return new string[] { };
}
}
}
DocumentStatusController
The DocumentStatusController provides the API endpoints:
/api/status (GET)for getting document metadata and status/api/status/{id} (DELETE)for deleting a document from the Search Index/api/status/{id}/indexto re-schedule a document for indexing
This boils down to the following implementation:
// Copyright (c) Philipp Wagner. All rights reserved.
// Licensed under the MIT license. See LICENSE file in the project root for full license information.
using ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web.Contracts;
using ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web.Database.Factory;
using ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web.Database.Model;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Data;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web.Controllers
{
public class DocumentStatusController : Controller
{
private readonly ApplicationDbContextFactory applicationDbContextFactory;
public DocumentStatusController(ApplicationDbContextFactory applicationDbContextFactory)
{
this.applicationDbContextFactory = applicationDbContextFactory;
}
[HttpGet]
[Route("/api/status")]
public async Task<IActionResult> Query(CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
var documentStatusList = await GetDocumentStatusListAsync(cancellationToken);
return Ok(documentStatusList);
}
private async Task<List<DocumentStatusDto>> GetDocumentStatusListAsync(CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
using (var context = applicationDbContextFactory.Create())
{
using (var transaction = await context.Database.BeginTransactionAsync(System.Data.IsolationLevel.ReadCommitted))
{
return await context.Documents
// Project, so we do not load binary data:
.Select(document => new DocumentStatusDto
{
Id = document.Id,
Title = document.Title,
Filename = document.Filename,
IsOcrRequested = document.IsOcrRequested,
Status = ConvertStatusEnum(document.Status)
})
// Order By ID for now:
.OrderBy(x => x.Id)
// Do not track this query
.AsNoTracking()
// Evaluate Asynchronously:
.ToListAsync(cancellationToken);
}
}
}
[HttpDelete]
[Route("/api/status/{id}")]
public async Task<IActionResult> Delete(int id, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
using (var context = applicationDbContextFactory.Create())
{
using (var transaction = await context.Database.BeginTransactionAsync())
{
var document = await context.Documents.FirstAsync(x => x.Id == id, cancellationToken);
if (document == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
if (document.Status != StatusEnum.Deleted)
{
document.Status = StatusEnum.ScheduledDelete;
await context.SaveChangesAsync(cancellationToken);
await transaction.CommitAsync(cancellationToken);
}
}
}
return Ok();
}
[HttpPost]
[Route("/api/status/{id}/index")]
public async Task<IActionResult> Index(int id, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
using (var context = applicationDbContextFactory.Create())
{
using (var transaction = await context.Database.BeginTransactionAsync())
{
var document = await context.Documents.FirstAsync(x => x.Id == id, cancellationToken);
if (document == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
document.Status = StatusEnum.ScheduledIndex;
await context.SaveChangesAsync(cancellationToken);
await transaction.CommitAsync(cancellationToken);
}
}
return Ok();
}
private static StatusEnumDto ConvertStatusEnum(StatusEnum status)
{
switch(status)
{
case StatusEnum.None:
return StatusEnumDto.None;
case StatusEnum.ScheduledIndex:
return StatusEnumDto.ScheduledIndex;
case StatusEnum.ScheduledDelete:
return StatusEnumDto.ScheduledDelete;
case StatusEnum.Indexed:
return StatusEnumDto.Indexed;
case StatusEnum.Failed:
return StatusEnumDto.Failed;
case StatusEnum.Deleted:
return StatusEnumDto.Deleted;
default:
return StatusEnumDto.None;
}
}
}
}
HomeController
To serve the Angular application We are providing the HomeController, that will be configured as the Fallback Controller in
the ASP.NET Core Startup code:
Adds a specialized
RouteEndpointto theIEndpointRouteBuilderthat will match requests for non-file-names with the lowest possible priority. The request will be routed to a controller endpoint that matches action, and controller.
If the route matches, it will serve the Angular index.html from the wwwroot directory:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using System.IO;
namespace ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web.Controllers
{
public class HomeController : Controller
{
private readonly IWebHostEnvironment environment;
public HomeController(IWebHostEnvironment environment)
{
this.environment = environment;
}
public IActionResult Index()
{
return PhysicalFile(Path.Combine(environment.ContentRootPath, environment.WebRootPath, "index.html"), "text/html");
}
}
}
Startup
An ASP.NET Core application requires us to define a so called Startup class, where all Application Services,
Configurations and Options are registered for Dependency Injection. At the same time we are also adding the
Background Services for the Hosting environment and configure the HTTP Request Pipeline.
The Microsoft documentation writes on the Startup class:
ASP.NET Core apps use a
Startupclass, which is named Startup by convention. The Startup class:
- Optionally includes a
ConfigureServicesmethod to configure the app's services. A service is a reusable component that provides app functionality. Services are registered inConfigureServicesand consumed across the app via dependency injection (DI) or ApplicationServices.- Includes a
Configuremethod to create the app's request processing pipeline.
ConfigureServicesandConfigureare called by the ASP.NET Core runtime when the app starts:
So long story short, here is the Startup for our Search application.
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.DataProtection;
using System.IO;
using ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web.Elasticsearch;
using ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web.Options;
using ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web.Services;
using ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web.Hosting;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web.Database.Context;
using ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web.Database.Factory;
namespace ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web
{
public class Startup
{
public Startup(IConfiguration configuration)
{
Configuration = configuration;
}
public IConfiguration Configuration { get; }
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
// Add CORS:
services.AddCors(options =>
{
options.AddPolicy("CorsPolicy", policyBuilder =>
{
policyBuilder
.WithOrigins("http://localhost:4200", "http://localhost:9000")
.SetIsOriginAllowedToAllowWildcardSubdomains()
.AllowAnyMethod()
.AllowAnyHeader()
.AllowCredentials();
;
});
});
// Use the Options Module:
services.AddOptions();
// Configure all Options Here:
ConfigureOptions(services);
// Configures Database-related logic:
ConfigureDbContext(services);
// Register Hosted Services:
RegisterHostedServices(services);
// Register Application Specific Services here:
RegisterApplicationServices(services);
// Data Protection-related stuff goes here:
ConfigureDataProtection(services);
// Use Web Controllers:
services.AddControllers();
// MVC for Controllers:
services.AddMvc();
}
// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to configure the HTTP request pipeline.
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env)
{
if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
}
app.UseCors("CorsPolicy");
app.UseAuthentication();
app.UseRouting();
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseAuthorization();
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints.MapControllerRoute(
name: "default",
pattern: "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}");
endpoints.MapFallbackToController("Index", "Home");
});
}
private void ConfigureOptions(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.Configure<ApplicationOptions>(Configuration.GetSection("Application"));
services.Configure<TesseractOptions>(Configuration.GetSection("Application:Tesseract"));
services.Configure<ElasticsearchOptions>(Configuration.GetSection("Application:Elasticsearch"));
services.Configure<IndexerOptions>(Configuration.GetSection("Application:Indexer"));
}
private void RegisterApplicationServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddSingleton<ElasticsearchClient>();
services.AddSingleton<TesseractService>();
services.AddSingleton<ElasticsearchIndexService>();
}
private void RegisterHostedServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddHostedService<DatabaseInitializerHostedService>();
services.AddHostedService<ElasticsearchInitializerHostedService>();
services.AddHostedService<DocumentIndexerHostedService>();
}
private void ConfigureDataProtection(IServiceCollection services)
{
var keyDirectory = Configuration.GetValue<string>("Application:DataProtection:Directory");
// Use a fixed Machine Key, so the Machine Key isn't regenerated for each restart:
services.AddDataProtection()
.SetApplicationName("sample-app")
.PersistKeysToFileSystem(new DirectoryInfo(keyDirectory));
}
private void ConfigureDbContext(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddDbContext<ApplicationDbContext>(builder => builder
.UseNpgsql(Configuration.GetConnectionString("DocumentDatabase"), x => x.MigrationsAssembly("ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web").CommandTimeout(10)));
// Add the DbContextOptions:
var dbContextOptions = new DbContextOptionsBuilder<ApplicationDbContext>()
.UseNpgsql(Configuration.GetConnectionString("DocumentDatabase"), x => x.MigrationsAssembly("ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web").CommandTimeout(10))
.Options;
// Construct the Factory, so we do not have do deal with DI Lifetime Scopes when instantiating the Context:
var dbContextFactory = new ApplicationDbContextFactory(dbContextOptions);
services.AddSingleton(dbContextFactory);
}
}
}
Creating the Web Host
And finally define the Entry Point for the Webservice, which creates the Host using the ASP.NET Core HostBuilder. I want the sample to
use IIS Express by adding UseIISIntegration and have it listen to port 9000 by using UseUrls("http://*:9000"):
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting;
using System.IO;
namespace ElasticsearchFulltextExample.Web
{
public class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
CreateHostBuilder(args).Build().Run();
}
public static IHostBuilder CreateHostBuilder(string[] args) =>
Host.CreateDefaultBuilder(args)
.ConfigureWebHostDefaults(webBuilder =>
{
webBuilder
.UseContentRoot(Directory.GetCurrentDirectory())
.UseWebRoot("wwwroot")
.UseUrls("http://*:9000")
.UseIISIntegration()
.UseStartup<Startup>();
});
}
}
appsettings.json
All Options are read from the appsettings.json file, where you define the:
- Database Connection String
- Elasticsearch Index Name and Endpoint
- Tesseract Executable and Temporary Directory
- Logging Levels
On my system the SSD is on the G: device, so I installed Elasticsearch and Postgres there:
{
"ConnectionStrings": {
"DocumentDatabase": "Server=127.0.0.1;Port=5432;Database=sampledb;User Id=philipp;Password=test_pwd;"
},
"Application": {
"BaseUri": "http://localhost:9000",
"Tesseract": {
"Executable": "\"C:\\Program Files\\Tesseract-OCR\\tesseract.exe\"",
"TempDirectory": "G:\\Data\\Tesseract"
},
"DataProtection": {
"Directory": "G:\\Data\\Keys"
},
"Elasticsearch": {
"Uri": "http://localhost:9200",
"IndexName": "documents"
},
"Indexer": {
"IndexDelay": 10
}
},
"Logging": {
"LogLevel": {
"Default": "Information",
"Microsoft": "Warning",
"Microsoft.Hosting.Lifetime": "Information"
}
},
"AllowedHosts": "*"
}
Conclusion
And that's it.
You now have a Fulltext Search application example for a Frontend and a Backend with ASP.NET Core and Angular 9!
Start your Elasticsearch server and PostgreSQL database, add some documents and explore what's possible. 👍
License
All code is released under terms of the MIT License.